我们知道platform_device和platform_driver匹配后,就会执行platform_driver中的匹配函数,那platform_device是如何来的呢?
实际上,platform_device是由设备树中的节点转换来的,什么时候转换以及如何转换的就是本文的主要内容。
了解内核启动过程的朋友对于start_kernel()这个函数应该不陌生,在start_kernel()的最后调用了rest_init()函数,依次往下调用执行,最后循环执行一个数组里的函数。
start_kernel // init/main.c
rest_init();
pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
kernel_init
kernel_init_freeable();
do_basic_setup();
do_initcalls();
for (level = 0; level < ARRAY_SIZE(initcall_levels) - 1; level++)
do_initcall_level(level); // 比如 do_initcall_level(3)
for (fn = initcall_levels[3]; fn < initcall_levels[3+1]; fn++)
do_one_initcall(initcall_from_entry(fn)); // 就是调用"arch_initcall_sync(fn)"中定义的fn函数接下来我们看这个数组里的函数,会发现在代码中找不到,原因是这些函数在链接的时候放在了initcall代码段中。
#define __define_initcall(fn, id) \
static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used \
__attribute__((__section__(".initcall" #id ".init"))) = fn; 在linux内核源码中,同系列的调用声明还有:
#define pure_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 0) #define core_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1) #define core_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1s) #define postcore_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2) #define postcore_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2s) #define arch_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3) #define arch_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3s) #define subsys_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4) #define subsys_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4s) #define fs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5) #define fs_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5s) #define rootfs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, rootfs) #define device_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6) #define device_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6s) #define late_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7) #define late_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7s)
这些宏最终都是调用__define_initcall(fn, n),这个数字代表系统启动时被调用的优先级,数字越小,优先级越低,用这一系列宏声明一个新的函数就是将这个函数指针放入内存中一个指定的段内。
编译内核,section属性的变量(.initcalln.init)会被集中放在一起,放在linux内核目录下include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h文件中,linux内核启动时会从何里面取出section属性(.initcalln.init,n代表优先级)会依次调用这些段中的函数。vmlinux.lds.h中定义如下所示:
#define INIT_CALLS \ __initcall_start = .; \ KEEP(*(.initcallearly.init)) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(0) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(1) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(2) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(3) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(4) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(5) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(rootfs) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(6) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(7) \ __initcall_end = .;
static void __init do_pre_smp_initcalls(void)
{
initcall_entry_t *fn;
trace_initcall_level("early");
for (fn = __initcall_start; fn < __initcall0_start; fn++)
do_one_initcall(initcall_from_entry(fn));
}这里将.initcall段的首地址赋值给fn函数进行执行,执行 fn时就会执行代码段里对应的代码。
那么回到我们platform_device转换这边,是启动的时候代码段里调用的下面这个函数of_platform_default_populate_init:
arch_initcall_sync(of_platform_default_populate_init);
在of_platform_default_populate_init这个函数中,首先判断是否已经迁移过设备树了,如果迁移过了就直接返回失败。然后对reserved_mem_matches[]这个数组里的节点调用of_platform_device_create()创建对应的platform_device。
static int __init of_platform_default_populate_init(void)
{
struct device_node *node;
if (!of_have_populated_dt())
return -ENODEV;
/*
* Handle certain compatibles explicitly, since we don't want to create
* platform_devices for every node in /reserved-memory with a
* "compatible",
*/
for_each_matching_node(node, reserved_mem_matches) //处理一些保留的节点
of_platform_device_create(node, NULL, NULL);
node = of_find_node_by_path("/firmware"); //处理/firmware下面的子节点
if (node) {
of_platform_populate(node, NULL, NULL, NULL);
of_node_put(node);
}
/* Populate everything else. 处理所有的信息 */
of_platform_default_populate(NULL, NULL, NULL); --------1
return 0;
}再后面到函数of_platform_populate后,出现两个条件情况
第一个 root = node = of_find_node_by_path(“/firmware”);
第二个 root = of_find_node_by_path(“/”) + of_default_bus_match_table[]
然后执行 of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);
第一种情况:child 从 “/firmware” 节点开始找,没有match限制。
node = of_find_node_by_path("/firmware");
if (node) {
of_platform_populate(node, NULL, NULL, NULL);
of_node_put(node);
}int of_platform_populate(struct device_node *root,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,
struct device *parent)
{
struct device_node *child;
int rc = 0;
root = root ? of_node_get(root) : of_find_node_by_path("/");
if (!root)
return -EINVAL;
pr_debug("%s()\n", __func__);
pr_debug(" starting at: %pOF\n", root);
device_links_supplier_sync_state_pause();
for_each_child_of_node(root, child) {
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
}
device_links_supplier_sync_state_resume();
of_node_set_flag(root, OF_POPULATED_BUS);
of_node_put(root);
return rc;
}node为/firmware,matches, lookup, parent都为NULL,则依次给/firmware/下每个子节点创建platform_data。
第二种情况:of_platform_default_populate(NULL, NULL, NULL); 再调用of_platform_populate(root, of_default_bus_match_table, lookup,
parent); 这时候传入的match就不是NULL了,而变成了of_default_bus_match_table这个数组,
所以child 从 “/” 节点开始找,有match限制。
这两种情况中,通常第二点作为创建platform device的主要规则。所以这里也以第二种情况来分析。
我们先看下这个of_default_bus_match_table的内容:
const struct of_device_id of_default_bus_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "simple-bus", },
{ .compatible = "simple-mfd", },
{ .compatible = "isa", },
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_AMBA
{ .compatible = "arm,amba-bus", },
#endif /* CONFIG_ARM_AMBA */
{} /* Empty terminated list */
};of_platform_populate()中对 / 节点下每一个子节点调用of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);进行处理:
static int of_platform_bus_create(struct device_node *bus,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,
struct device *parent, bool strict)
{
const struct of_dev_auxdata *auxdata;
struct device_node *child;
struct platform_device *dev;
const char *bus_id = NULL;
void *platform_data = NULL;
int rc = 0;
/* Make sure it has a compatible property */
if (strict && (!of_get_property(bus, "compatible", NULL))) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %pOF, no compatible prop\n",
__func__, bus);
return 0;
}
/* Skip nodes for which we don't want to create devices */
if (unlikely(of_match_node(of_skipped_node_table, bus))) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %pOF node\n", __func__, bus);
return 0;
}
if (of_node_check_flag(bus, OF_POPULATED_BUS)) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %pOF, already populated\n",
__func__, bus);
return 0;
}
auxdata = of_dev_lookup(lookup, bus);
if (auxdata) {
bus_id = auxdata->name;
platform_data = auxdata->platform_data;
}
if (of_device_is_compatible(bus, "arm,primecell")) {
/*
* Don't return an error here to keep compatibility with older
* device tree files.
*/
of_amba_device_create(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);
return 0;
}
dev = of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);
if (!dev || !of_match_node(matches, bus))
return 0;
for_each_child_of_node(bus, child) {
pr_debug(" create child: %pOF\n", child);
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, &dev->dev, strict);
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
}
of_node_set_flag(bus, OF_POPULATED_BUS);
return rc;
}在上面的of_platform_bus_create函数中,首先判断/目录下该子节点是否有compatible属性,如果有,没有则直接返回,继续处理/目录下其他子节点。
/* Skip nodes for which we don't want to create devices */
if (unlikely(of_match_node(of_skipped_node_table, bus))) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %pOF node\n", __func__, bus);
return 0;
}跳过一些我们不想创建平台设备的节点,可以放在of_skipped_node_table数组中,如果当前子节点与of_skipped_node_table数组中的匹配,则跳过该节点返回继续处理/目录下其他子节点。
if (of_node_check_flag(bus, OF_POPULATED_BUS)) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %pOF, already populated\n",
__func__, bus);
return 0;
}如果当前子节点的FLAG为OF_POPULATED_BUS,表面该节点已经转换过了,不需要再处理了,跳过该子节点返回继续处理/目录下其他子节点。
if (of_device_is_compatible(bus, "arm,primecell")) {
of_amba_device_create(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);
return 0;
}
compatilble属性为 arm,primecell ,创建完平台设备就返回,不处理该子节点下的子节点。
然后下面就到了真正创建本子节点为平台设备的函数,稍后我们再来展开看这个函数具体怎么把该子节点转换为平台设备的。
dev = of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);
接着就到了上一层matches传入的of_default_bus_match_table数组,判断该数组中是否包含本节点,如果不包含,就返回,也就是不再处理该子节点下的子节点了。所以of_default_bus_match_table包含的子节点只转换该子节点,不转换子节点下面的子节点。
if (!dev || !of_match_node(matches, bus))
return 0;
for_each_child_of_node(bus, child) {
pr_debug(" create child: %pOF\n", child);
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, &dev->dev, strict);
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
接下来我们就看最重要的函数of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent):、
static struct platform_device *of_platform_device_create_pdata(
struct device_node *np,
const char *bus_id,
void *platform_data,
struct device *parent)
{
struct platform_device *dev;
if (!of_device_is_available(np) ||
of_node_test_and_set_flag(np, OF_POPULATED))
return NULL;
dev = of_device_alloc(np, bus_id, parent);
if (!dev)
goto err_clear_flag;
dev->dev.coherent_dma_mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(32);
if (!dev->dev.dma_mask)
dev->dev.dma_mask = &dev->dev.coherent_dma_mask;
dev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;
dev->dev.platform_data = platform_data;
of_msi_configure(&dev->dev, dev->dev.of_node);
of_reserved_mem_device_init_by_idx(&dev->dev, dev->dev.of_node, 0);
if (of_device_add(dev) != 0) {
platform_device_put(dev);
goto err_clear_flag;
}
return dev;
err_clear_flag:
of_node_clear_flag(np, OF_POPULATED);
return NULL;
}在这个函数中,先判断节点是否存在,是否已经迁移过了,然后给dev这个平台设备分配空间,填充里边的部分数据,最后调用of_device_add()来添加设备。
of_device_add调用device_add(&ofdev->dev);
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
struct kobject *glue_dir = NULL;
dev = get_device(dev);//增加设备的引用计数 dev->kobj->kref
if (!dev)
goto done;
if (!dev->p) {
error = device_private_init(dev);//私有数据没有的话申请并初始化,这个数据很重要,它是连接所属bus,parent,对应驱动等的重要连接点.
if (error)
goto done;
}
/*
* for statically allocated devices, which should all be converted
* some day, we need to initialize the name. We prevent reading back
* the name, and force the use of dev_name()
*/
if (dev->init_name) {
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);//用dev的init_name初始化dev-kobject->name,实际就是目录名。
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name) //dev的init_name不存在且dev-kobject->name也不存在,则使用bus的dev_name和dev_id来设置目录名
dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);
if (!dev_name(dev)) { //如果上面几个步骤都还没找到可设的目录名,则失败返回,设备必须要放在某个目录下。
error = -EINVAL;
goto name_error;
}
pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);
parent = get_device(dev->parent); //父节点引用计数加1
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent); //拿到父节点
if (IS_ERR(kobj)) {
error = PTR_ERR(kobj);
goto parent_error;
}
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj; //拿到的父节点赋值给本dev->kobj.parent,确定设备父子关系,也确定了sysfs中的目录关系
/* use parent numa_node */
if (parent && (dev_to_node(dev) == NUMA_NO_NODE))
set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent)); //设置该设备节点为-1,一般未注册前在device_initialize已经初始化为-1
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);//把内嵌的kobject注册到设备模型中将设备加入到kobject模型中,创建sys相关目录,目录名字为kobj->name
if (error) {
glue_dir = get_glue_dir(dev);
goto Error;
}
/* notify platform of device entry */
if (platform_notify)
platform_notify(dev);
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent); /*创建sys目录下设备的uevent属性文件,通过它可以查看设备的uevent事件,主要是在/sys/devices/.../中添加dev的uevent属性文件*/
if (error)
goto attrError;
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev); /*实际创建的kobject都是在device下面,其他class,bus之类的里面的具体设备都是device目录下设备的符号链接,这里是在class下创建符号链接 */
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev); //创建sys目录下设备其他属性文件(添加设备属性文件)
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
error = bus_add_device(dev); //添加设备的总线属性,将设备加入到管理它的bus总线的设备连表上,创建subsystem链接文件,链接class下的具体的子系统文件夹 将设备添加到其总线的设备列表中。
if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev); ;//把设备增加到sysfs电源管理power目录(组)下,如果该设备设置电源管理相关的内容
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev); //设备添加到电源管理相关的设备列表中
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) { /* 主设备号存在,则产生dev属性,并在/dev目录下产生设备节点文件 */
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
if (error)
goto DevAttrError;
/*在/sys/dev/char/或者/sys/dev/block/创建devt的属性的连接文件,形如10:45,由主设备号和次设备号构成,指向/sys/devices/.../的具体设备目录*/
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev); //该链接文件只具备读属性,显示主设备号:次设备号,如10:45,用户空间udev响应uevent事件时,将根据设备号在/dev下创建节点文件
if (error)
goto SysEntryError;
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
if (dev->bus) //通知客户端,有新设备加入
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
/*产生一个内核uevent事件(这里是有设备加入),可以是helper,也可是通过netlink机制和用户空间通信该事件可以被内核以及应用层捕获,属于linux设备模型中热插拔机制*/
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
/*
* Check if any of the other devices (consumers) have been waiting for
* this device (supplier) to be added so that they can create a device
* link to it.
*
* This needs to happen after device_pm_add() because device_link_add()
* requires the supplier be registered before it's called.
*
* But this also needs to happen before bus_probe_device() to make sure
* waiting consumers can link to it before the driver is bound to the
* device and the driver sync_state callback is called for this device.
*/
if (dev->fwnode && !dev->fwnode->dev) {
dev->fwnode->dev = dev;
fw_devlink_link_device(dev);
}
bus_probe_device(dev); //给设备探测寻找相对应的驱动,在bus上找dev对应的drv,主要执行__device_attach,主要进行match,sys_add,执行probe函数和绑定等操作
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,
&parent->p->klist_children); //添加新设备到父设备的子列表中
if (dev->class) { //如果该dev有所属类,则将dev的添加到类的设备列表里面
mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->mutex); //要使用class的互斥锁
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->knode_class,
&dev->class->p->klist_devices); //dev添加到class的klist_device链表(对driver也有klist_driver链表)
/*通知有新设备加入,执行该dev的class_intf->add_dev(),好处是只有设备匹配注册成功了,才进行其它的注册工作(如字符设备的注册,生成/dev/***节点文件)以及部分初始化工作。*/
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
list_for_each_entry(class_intf,
&dev->class->p->interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);
mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
}
done:
put_device(dev);
return error;
SysEntryError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
DevAttrError:
device_pm_remove(dev);
dpm_sysfs_remove(dev);
DPMError:
bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:
device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:
device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
attrError:
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);
glue_dir = get_glue_dir(dev);
kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:
cleanup_glue_dir(dev, glue_dir);
parent_error:
put_device(parent);
name_error:
kfree(dev->p);
dev->p = NULL;
goto done;
}简单来讲,就是里面创建一些关于这个设备的目录和文件,然后去匹配现有的驱动力有没有能匹配上的,然后再创建字符设备。
创建完平台设备后会去平台驱动的列表里匹配看看有没有能够匹配得上的平台驱动,就是bus_probe_device(dev)
void bus_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = dev->bus;
struct subsys_interface *sif;
if (!bus) //确定总线存在,否则出错返回
return;
if (bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) //drivers_autoprobe是一个bit变量,为l则允许本条总线上的device注册时自动匹配driver,drivers_autoprobe默认总是为1,除非用户空间修改
device_initial_probe(dev);
mutex_lock(&bus->p->mutex);
list_for_each_entry(sif, &bus->p->interfaces, node)
if (sif->add_dev)
sif->add_dev(dev, sif);
mutex_unlock(&bus->p->mutex);
}device_initial_probe调用__device_attach(dev, true):
static int __device_attach(struct device *dev, bool allow_async)
{
int ret = 0;
device_lock(dev);
if (dev->p->dead) {
goto out_unlock;
} else if (dev->driver) { //如果driver已经放在device了(初始化device,时,手动添加的driver)
if (device_is_bound(dev)) { //判断设备是否已经绑定过了,绑定过了退出,没绑定过执行下面的device_bin_driver绑定
ret = 1;
goto out_unlock;
}
ret = device_bind_driver(dev);
if (ret == 0)
ret = 1;
else {
dev->driver = NULL;
ret = 0;
}
} else { //刚注册的device,没有添加对应的driver,需要查找匹配对应的驱动
struct device_attach_data data = {
.dev = dev,
.check_async = allow_async,
.want_async = false,
};
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
ret = bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data,
__device_attach_driver); //遍历总线上的driver链表,一个一个进行匹配
if (!ret && allow_async && data.have_async) {
/*
* If we could not find appropriate driver
* synchronously and we are allowed to do
* async probes and there are drivers that
* want to probe asynchronously, we'll
* try them.
*/
dev_dbg(dev, "scheduling asynchronous probe\n");
get_device(dev);
async_schedule(__device_attach_async_helper, dev);
} else {
pm_request_idle(dev);
}
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);
}
out_unlock:
device_unlock(dev);
return ret;
}int device_bind_driver(struct device *dev)
{
int ret;
ret = driver_sysfs_add(dev); //把dev和driver链接起来
if (!ret)
driver_bound(dev); //device里面私有的driver节点挂接到driver的设备链表(一个driver可能对应多个device)
else if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_DRIVER_NOT_BOUND, dev);
return ret;
}static int driver_sysfs_add(struct device *dev)
{
int ret;
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,//通知其它总线将要绑定driver 到device
BUS_NOTIFY_BIND_DRIVER, dev);
ret = sysfs_create_link(&dev->driver->p->kobj, &dev->kobj,
kobject_name(&dev->kobj));//在driver目录下创建device目录的符号链接,名字为设备的名字
if (ret == 0) {
ret = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj, &dev->driver->p->kobj,
"driver");//在device目录下创建driver的目录,名字为driver
if (ret)
sysfs_remove_link(&dev->driver->p->kobj,
kobject_name(&dev->kobj));
}
return ret;
}static void driver_bound(struct device *dev)
{
if (device_is_bound(dev)) { //再次检查,确定没绑定
printk(KERN_WARNING "%s: device %s already bound\n",
__func__, kobject_name(&dev->kobj));
return;
}
pr_debug("driver: '%s': %s: bound to device '%s'\n", dev->driver->name,
__func__, dev_name(dev));
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_driver, &dev->driver->p->klist_devices); /* 绑定!!!!!! 把device私有的p里的knode_driver,绑定到driver里面的klist_device链表上 */
device_links_driver_bound(dev);
device_pm_check_callbacks(dev);
/*
* Make sure the device is no longer in one of the deferred lists and
* kick off retrying all pending devices
*/
driver_deferred_probe_del(dev);
driver_deferred_probe_trigger();
if (dev->bus) //通知其它子模块以及绑定成功
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_BOUND_DRIVER, dev);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_BIND);
}至此,设备和驱动的绑定工作完成了,我们再回到前面如果设备没有匹配绑定驱动,则遍历总线寻找可以匹配的驱动。
__device_attach_driver=》driver_match_device(drv, dev)
static int __device_attach_driver(struct device_driver *drv, void *_data)
{
struct device_attach_data *data = _data;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
bool async_allowed;
int ret;
ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev);
if (ret == 0) { //如果匹配不上,就返回
/* no match */
return 0;
} else if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) { //匹配出错
dev_dbg(dev, "Device match requests probe deferral\n");
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
} else if (ret < 0) { //匹配出错
dev_dbg(dev, "Bus failed to match device: %d", ret);
return ret;
} /* ret > 0 means positive match */
async_allowed = driver_allows_async_probing(drv);
if (async_allowed)
data->have_async = true;
if (data->check_async && async_allowed != data->want_async)
return 0;
return driver_probe_device(drv, dev);//前面匹配成功,则调用匹配的驱动的probe函数
}static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *dev)
{
return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
}匹配的时候判断平台驱动的match函数是否存在,如果平台总线的match存在,则调用平台总线的match函数,那平台总线的match函数在哪里呢?
我们以led驱动的注册为例,在led-gpio中,通过module_platform_driver(gpio_led_driver)注册了一个驱动,实际上module_platform_driver是个宏定义,在platform_device.h中:
#define platform_driver_register(drv) \ __platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
展开后,就是:
int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv,
struct module *owner)
{
drv->driver.owner = owner;
drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;
drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;
drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;
drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;
return driver_register(&drv->driver);
}在这里就看到了平台总线驱动的drv->driver.bus,所以driver_match_device()中的drv->bus->match就是platform_bus_type中的match,我们打开platform_bus_type来看一下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.dma_configure = platform_dma_configure,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};就是调用的这里的platform_match函数:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
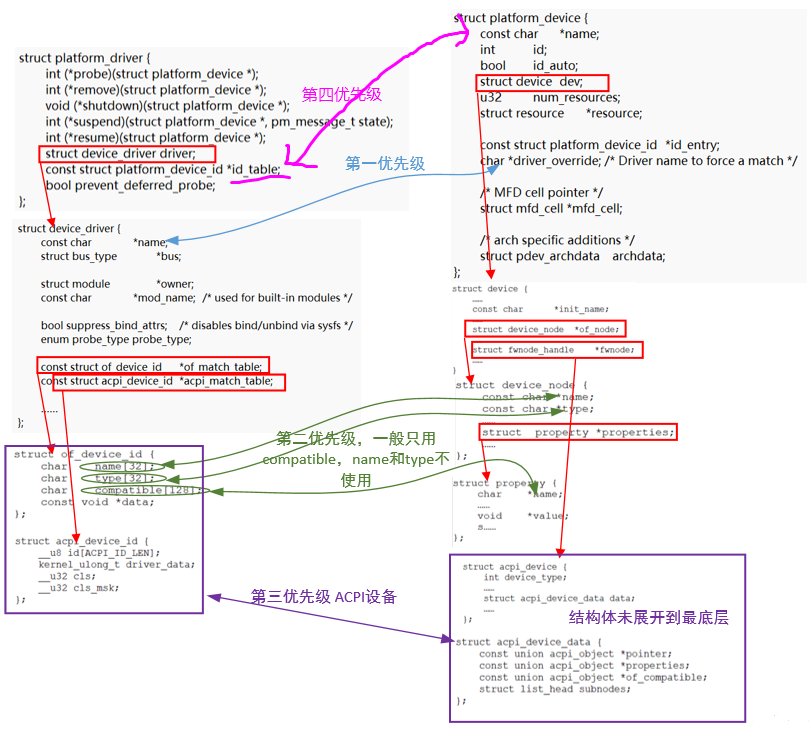
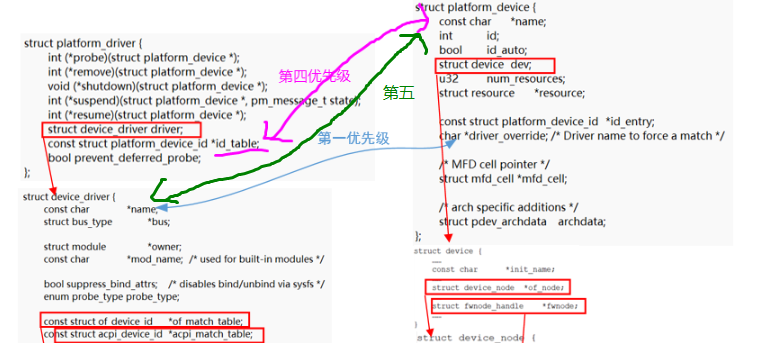
}(1)如果设置了driver_override,即driver_override不为NULL,那么只会进行driver_override的匹配,其优先级是最高的:

(2)设备树的匹配从of_driver_match_device开始分析,其函数调用关系如下:
of_driver_match_device(struct device *dev,const struct device_driver *drv) -->of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, dev) ---->of_match_node(matches, dev->of_node); ------>__of_match_node(matches, node); -------->__of_device_is_compatible(node, matches->compatible,matches->type, matches->name);
分析内核代码可以得到设备树匹配比较的具体对象,其中device的device_node信息是通过解析设备树的节点得到的:
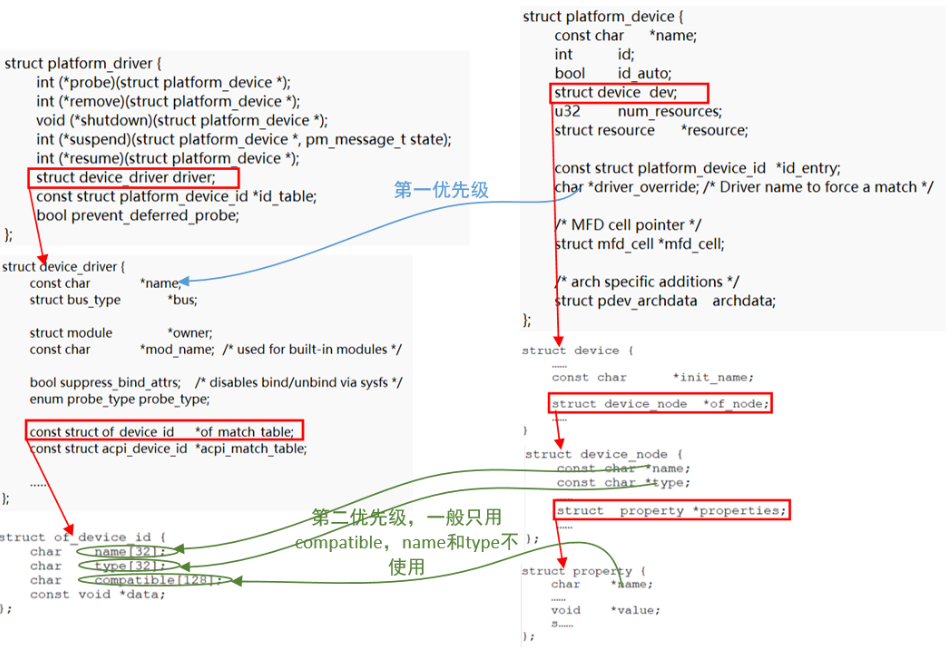
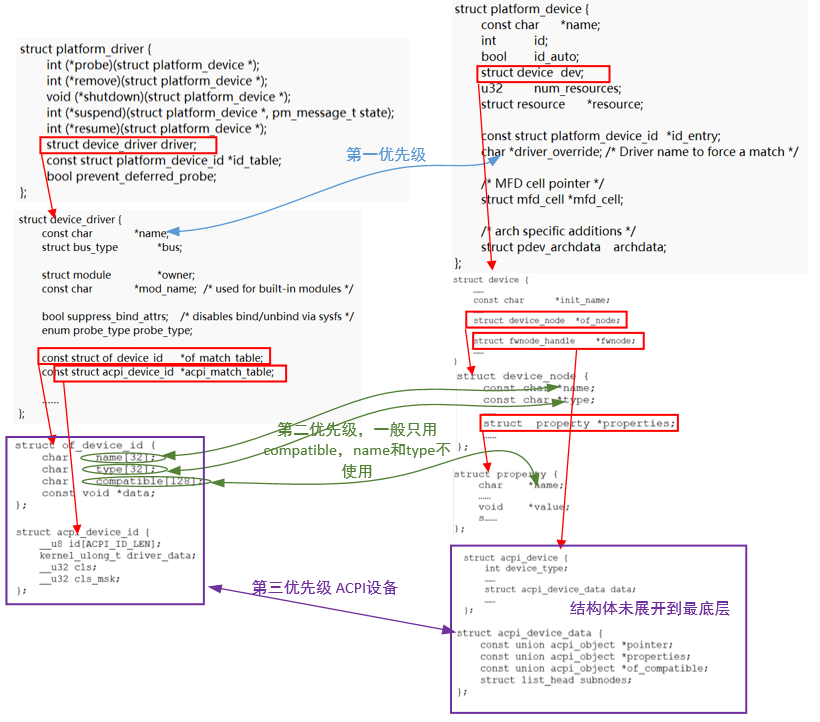
(3)acpi的驱动在开发中没有使用到过,在此仅做简单分析,其代码调用如下,当没有设置acpi_match_table的时候会调用acpi_of_match_device进行匹配,设置了acpi_match_table的话会调用__acpi_match_device进行匹配:
bool acpi_driver_match_device(struct device *dev,
const struct device_driver *drv)
{
if (!drv->acpi_match_table)
return acpi_of_match_device(ACPI_COMPANION(dev),
drv->of_match_table);
return !!__acpi_match_device(acpi_companion_match(dev),
drv->acpi_match_table, drv->of_match_table);
}跟踪代码,其流程大致如下,后面的联合体内容较多未全部展开:
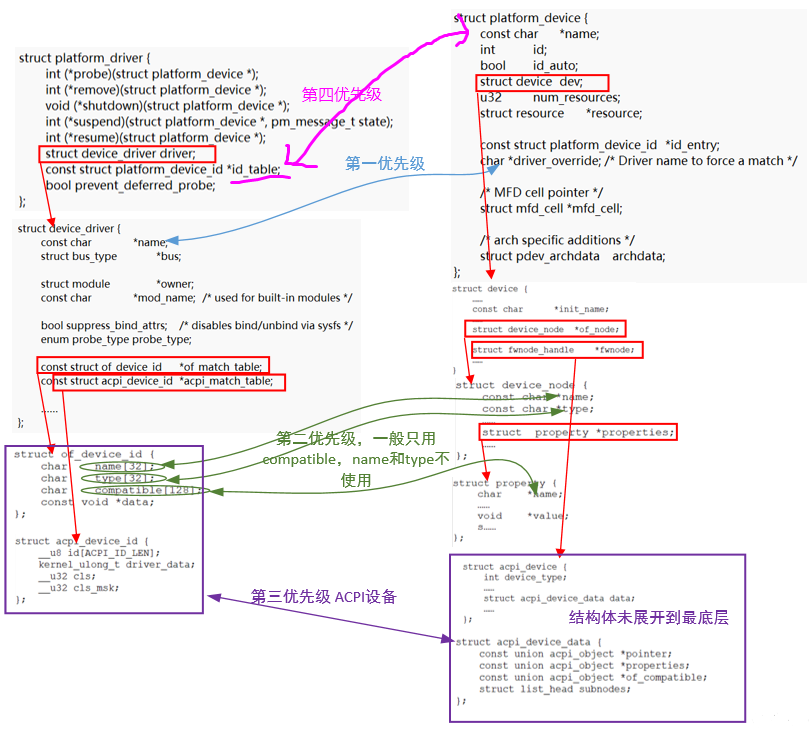
(4)id_table的匹配方式,平台驱动中的id_table->name与平台设备的name比较:
static const struct platform_device_id *platform_match_id(
const struct platform_device_id *id,
struct platform_device *pdev)
{
while (id->name[0]) {
if (strcmp(pdev->name, id->name) == 0) {
pdev->id_entry = id;
return id;
}
id++;
}
return NULL;
}
以上都不行的情况下,通过驱动的名称和平台设备的名称进行匹配:
/* fall-back to driver name match */ return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
匹配成功后,就会通过driver_probe_device(drv, dev)调用匹配的驱动的probe函数:
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
if (!device_is_registered(dev)) //通过查看在sysfs中的状态判断是都已经注册
return -ENODEV;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: matched device %s with driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
pm_runtime_get_suppliers(dev);
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
pm_runtime_barrier(dev);
if (initcall_debug)
ret = really_probe_debug(dev, drv);
else
ret = really_probe(dev, drv); //真正的probe
pm_request_idle(dev);
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);
pm_runtime_put_suppliers(dev);
return ret;
}static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret = -EPROBE_DEFER;
int local_trigger_count = atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count);
bool test_remove = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_TEST_DRIVER_REMOVE) &&
!drv->suppress_bind_attrs;
if (defer_all_probes) {
/*
* Value of defer_all_probes can be set only by
* device_defer_all_probes_enable() which, in turn, will call
* wait_for_device_probe() right after that to avoid any races.
*/
dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s force probe deferral\n", drv->name);
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
return ret;
}
ret = device_links_check_suppliers(dev);
if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER)
driver_deferred_probe_add_trigger(dev, local_trigger_count);
if (ret)
return ret;
atomic_inc(&probe_count);
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: probing driver %s with device %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, drv->name, dev_name(dev));
if (!list_empty(&dev->devres_head)) {
dev_crit(dev, "Resources present before probing\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto done;
}
re_probe:
dev->driver = drv; //匹配好后的驱动信息记录到设备内部
/* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */
ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);
if (ret)
goto pinctrl_bind_failed;
ret = dma_configure(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
if (driver_sysfs_add(dev)) { //driver加入sysfs(其实就是创建各种符号链接,前面device默认绑定有driver那里已经分析过了)
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_sysfs_add(%s) failed\n",
__func__, dev_name(dev));
goto probe_failed;
}
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->activate) {
ret = dev->pm_domain->activate(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
if (dev->bus->probe) { //如果总线上定义probe函数则调用
ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
} else if (drv->probe) { //否则调用驱动上的probe函数
ret = drv->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
if (test_remove) {
test_remove = false;
if (dev->bus->remove)
dev->bus->remove(dev);
else if (drv->remove)
drv->remove(dev);
devres_release_all(dev);
driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
dev->driver = NULL;
dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)
dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);
pm_runtime_reinit(dev);
goto re_probe;
}
pinctrl_init_done(dev);
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->sync)
dev->pm_domain->sync(dev);
driver_bound(dev); //将设备加入到驱动支持的设备链表中,一个设备需要一个驱动,一个驱动支持多个设备,前面device默认绑定driver那里已经分析过了
ret = 1;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: bound device %s to driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
goto done;
probe_failed:
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_DRIVER_NOT_BOUND, dev);
pinctrl_bind_failed:
device_links_no_driver(dev);
devres_release_all(dev);
dma_deconfigure(dev);
driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
dev->driver = NULL;
dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)
dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);
pm_runtime_reinit(dev);
dev_pm_set_driver_flags(dev, 0);
switch (ret) {
case -EPROBE_DEFER:
/* Driver requested deferred probing */
dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s requests probe deferral\n", drv->name);
driver_deferred_probe_add_trigger(dev, local_trigger_count);
break;
case -ENODEV:
case -ENXIO:
pr_debug("%s: probe of %s rejects match %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
break;
default:
/* driver matched but the probe failed */
printk(KERN_WARNING
"%s: probe of %s failed with error %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
}
/*
* Ignore errors returned by ->probe so that the next driver can try
* its luck.
*/
ret = 0;
done:
atomic_dec(&probe_count);
wake_up_all(&probe_waitqueue);
return ret;
}dev->bus->probe存在,所以执行dev->bus->probe,也就是platform下的platform_drv_probe
static int platform_drv_probe(struct device *_dev)
{
struct platform_driver *drv = to_platform_driver(_dev->driver); // 将传递给驱动程序的设备指针转换为 platform_driver 结构体指针
struct platform_device *dev = to_platform_device(_dev); // 将传递给驱动程序的设备指针转换为 platform_device 结构体指针
int ret;
ret = of_clk_set_defaults(_dev->of_node, false); // 设置设备节点的默认时钟属性
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
ret = dev_pm_domain_attach(_dev, true); // 将设备附加到电源域
if (ret)
goto out;
if (drv->probe) { //调用drv的probe函数
ret = drv->probe(dev);
if (ret)
dev_pm_domain_detach(_dev, true);
}
out:
if (drv->prevent_deferred_probe && ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
dev_warn(_dev, "probe deferral not supported\n");
ret = -ENXIO;
}
return ret;
}该函数的主要逻辑如下:
1 首先,将传递给驱动程序的设备指针 _dev 转换为 platform_driver 结构体指针 drv,将传递给驱动程序的设备指针 _dev 转换为 platform_device 结构体指针 dev。
2 使用 of_clk_set_defaults() 函数设置设备节点的默认时钟属性。这个函数会根据设备节点的属性信息配置设备的时钟。
3 调用 dev_pm_domain_attach() 将设备附加到电源域。这个函数会根据设备的电源管理需求,将设备与相应的电源域进行关联。
4 如果驱动程序的 probe 函数存在,调用它来执行设备的探测操作。drv->probe(dev) 表示调用驱动程序的 probe 函数,并传递 platform_device 结构体指针 dev 作为参数。如果探测失败,会调用 dev_pm_domain_detach() 分离设备的电源域。
5 处理探测延迟和错误情况。如果驱动程序设置了 prevent_deferred_probe 标志,并且返回值为 -EPROBE_DEFER,则表示探测被延迟。在这种情况下如果驱动程序设置了 prevent_deferred_probe 标志,并且返回值为 -EPROBE_DEFER,则表示探测被延迟。在这种情况下,代码会打印一个警告信息 probe deferral not supported,并将返回值设置为 -ENXIO,表示设备不存在。
总体而言,该函数的作用是执行平台驱动程序的探测操作,在设备上调用驱动程序的 probe 函数,并处理探测延迟和错误情况。
至此,开机启动后把设备树节点迁移为平台设备,并遍历总线驱动匹配的过程就完成。那如果是一开始没有驱动的情况,后面注册驱动的时候也是会去匹配设备的,我们在后面的文章中再来分析。